Short Notes Of computer Network
OSI Layers,data units and Functions:
| Layers | Data Units | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Application Layer | Data | Mail Services,Directory Serices,FTAM |
| Presentation Layer | Data | Encryption/Decryption, Compression |
| Session Layer | Data | Session Establishment, Synchronization,Dialog Controller |
| Transport Layer | Segments,Datagram | Segementation |
| Network Layer | Packets | Traffic control,Fragmentation,Routing |
| Data Link Layer | Frames | Flow control,Error control,Access control |
| Physical Layer | Bits | Bit Synchronization,Bit rate control,Physical Topologies |
Layers and their uses –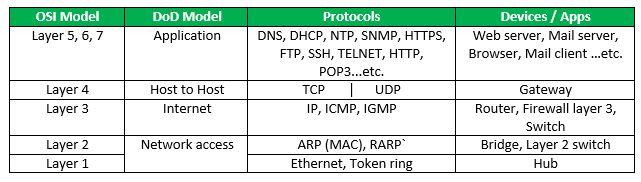
Physical Layer
- Mesh Topology:
In mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via particular channel.If suppose, N number of devices are connected with each other, then total number of links required to connect NC2. - Bus Topology:
Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to single cable. If N devices are connected, then the number of cables required 1 which is known as backbone cable and N drop lines are required. - Star Topology:
In star topology, all the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable. If N devices are connected to each other, then the no. of cables required N. - Ring Topology:
In this topology, it forms a ring connecting a devices with its exactly two neighboring devices.
- Simplex Mode: the communication is unidirectional, as on a one-way street.Only one of the two devices on a link can transmit, the other can only receive.
- Half-duplex Mode: each station can both transmit and receive, but not at the same time.
- Full-duplex Mode: both stations can transmit and receive simultaneously.
Manchester Encoding: When there is a long sequence of 0s and 1s, there is a problem at the receiving end. The problem is that the synchronization is lost due to lack of transmissions.
- NRZ-level encoding : The polarity of signals changes when incoming siganl changes from ‘1’ to ‘0’ or from ‘0’ to ‘1’. It considers the first bit data as polarity change.
- NRZ-Inverted/ Differential encoding:In this, the transitions at the beginning of bit interval is equal to 1 and if there is no transition at the beginning of bit interval is equal to 0.
Data Link Layer
- Flow Control
N = Sender’s Window Size. (in SR both sender and receiver window are same)
a = Tp /Tt
- Sequence No. >= (Sender’s Window Size) + (Reciever’s Window Size )
- Efficiency in TDM(polling) = Tt / (Tpoll + Tt)
- In CSMA/CD, Tt >= 2*Tp
Hence, min frame length = 2*Tp*B - In CSMA/CD, Efficiency = 1/(1 + 6.44a)
- Back-off Algorithm for CSMA/CD
Waiting time = back–off time
Let n = collision number or re-transmission serial number.
Then, Waiting time = K * Tslot
where K = [0, 2n – 1 ] - N = No. of stations
Early Token Reinsertion : Efficiency = 1/(1 + a/N)
Delayed Token Reinsertion : Efficiency = 1/(1 + (N+1)a/N) - Pure Aloha Efficiency = 18.4 %
Slotted Aloha Efficiency = 36.8% - Maximum data rate (channel capacity) for noiseless and noisy channels
- Noiseless Channel : Nyquist Bit Rate
BitRate = 2 * Bandwidth * log2(L)
where,L is the number of signal levels used to represent data. - Noisy Channel : Shannon Capacity
Capacity = bandwidth * log2(1 + SNR)
where, SNR is the signal-to-noise ratio
- Noiseless Channel : Nyquist Bit Rate
- Error Control
- Hamming Code: is a set of error-correction codes that can be used to detect and correct the errors that can occur when the data is moved or stored from the sender to the receiver.
Redundant bits:
2r ≥ m + r + 1
where, r = redundant bit, m = data bit - Framing in DLL: It provides a way for a sender to transmit a set of bits that are meaningful to the receiver.
Character/Byte Stuffing: Used when frames consist of character. If data contains ED then, byte is stuffed into data to diffentiate it from ED.
Bit stuffing: Sender stuffs a bit to break the pattern i.e. here appends a 0 in data = 011101.
Network Layer
Internet Control Message Protocol: Since IP does not have a inbuilt mechanism for sending error and control messages. It depends on Internet Control Message Protocol(ICMP) to provide an error control.
- Source quench message
- Parameter problem
- Time exceeded message
- Destination un-reachable
- Router having the highest router priority will be declared as DR.
- If there is a tie in router priority then highest router will be considered. First, highest loopback address is considered. If no loopback is configured then the highest active IP address on the interface of the router is considered.
- Hop count is the number of routers occurring in between the source and destination network. The path with the lowest hop count is considered as the best route to reach a network and therefore placed in the routing table.
- The maximum hop count allowed for RIP is 15 and hop count of 16 is considered as network unreachable.
Difference between DVR and LSR
Open shortest path first (OSPF): Open shortest path first (OSPF) is a link-state routing protocol which is used to find the best path between the source and the destination router using its own SPF algorithm.
Designated Router(DR) and Backup Designated Router(BDR) election takes place in broadcast network or multi-access network.
Criteria for the election:
Routing Information Protocol(RIP): is a dynamic routing protocol which uses hop count as a routing metric to find the best path between the source and the destination network. It is a distance vector routing protocol which has AD value 120 and works on the application layer of OSI model. RIP uses port number 520.
Hop Count :
Transport Layer
In TCP congestion control Algorithm
When Time Out Occurs Algorithm Enters Slow Start Phase
When 3 Duplicate occurs algorithm enters congestion avoidance phase
TCP 3-Way Handshake Process
Step 1 (SYN) : In the first step, client wants to establish a connection with server, so it sends a segment with SYN(Synchronize Sequence Number) which informs server that client is likely to start communication and with what sequence number it starts segments with
Step 2 (SYN + ACK): Server responds to the client request with SYN-ACK signal bits set. Acknowledgement(ACK) signifies the response of segment it received and SYN signifies with what sequence number it is likely to start the segments with
Step 3 (ACK) : In the final part client acknowledges the response of server and they both establish a reliable connection with which they will start eh actual data transfer.
Refer the Differences between TCP and UDP
Application Layer
Domain Name Server: DNS is a host name to IP address translation service. DNS is a distributed database implemented in a hierarchy of name servers. It is an application layer protocol for message exchange between clients and servers.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol(DHCP) is an application layer protocol which is used to provide:
Subnet Mask (Option 1 – e.g., 255.255.255.0)
Router Address (Option 3 – e.g., 192.168.1.1)
DNS Address (Option 6 – e.g., 8.8.8.8)
Vendor Class Identifier (Option 43 – e.g., ‘unifi’ = 192.168.1.9 ##where unifi = controller)
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) : SNMP is an application layer protocol which uses UDP port number 161/162.SNMP is used to monitor network, detect network faults and sometimes even used to configure remote devices.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP): SMTP is an application layer protocol. The client who wants to send the mail opens a TCP connection to the SMTP server and then sends the mail across the connection. The SMTP server is always on listening mode. As soon as it listens for a TCP connection from any client, the SMTP process initiates a connection on that port (25). After successfully establishing the TCP connection the client process sends the mail instantly.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): File Transfer Protocol(FTP) is an application layer protocol which moves files between local and remote file systems. It runs on the top of TCP, like HTTP. To transfer a file, 2 TCP connections are used by FTP in parallel: control connection and data connection.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP): is an application-level protocol that uses TCP as an underlying transport and typically runs on port 80. HTTP is a stateless protocol i.e. server maintains no information about past client requests.
Network Security
For Symmetric Key : n*(n-1)/2 keys are required.
For Public Key : 2*n key are required ( each node will have private and public key).
Deffie Hellman Key Exchange
R1 = gx mod p
R2 = gy mod q
Both will have same key = gxy mod p.




Comments
Post a Comment